CNN Library, May 30, 2015.
Here’s some background information about stem cells.
Scientists believe that stem cell research can be used to treat medical conditions including Parkinson’s Disease, spinal cord injury, stroke, burns, heart disease, diabetes, osteoarthritis, and rheumatoid arthritis.
About Stem Cells:
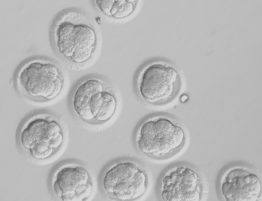
Stem cell research focuses on embryonic stem cells and adult stem cells. It is very experimental in humans. Embryonic stem cells are highly controversial. In order to harvest embryonic stem cells, the four to six day old embryo is destroyed. In 2005, researchers told a Congressional panel they would like to develop ways to remove only a single stem cell from an embryo without destroying it, but it is not known if something like this can succeed.
Stem cells have two characteristics that differentiate them from other types of cells:
– Stem cells are unspecialized cells that replicate themselves for long periods through cell division.
– Under certain physiologic or experimental conditions, stem cells can be induced to become mature cells with special functions, such as the beating cells of the heart muscle or insulin-producing cells of the pancreas.
There are four classes of stem cells: totipotent, multipotent, pluripotent, and unipotent.
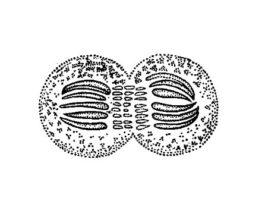
– Stem cells that develop into cells that make up all the cells in an embryo and fetus are calledtotipotent. (Ex: The zygote/fertilized egg and the cells at the very early stages following fertilization are considered totipotent)
– Multipotent stem cells can give rise to multiple types of cells, but all within a particular tissue, organ, or physiological system. (Ex: blood-forming stem cells/bone marrow cells, most often referred to as adult stem cells)
– Pluripotent stem cells (ex: embryonic stem cells) can give rise to any type of cell in the body. These cells are like blank slates, and they have the potential to turn into any type of cell.
– Stem cells that can self-renew as well as give rise to a single mature cell type are called unipotent. (Ex: sperm producing cells)
Embryonic stem cells are harvested from 4 to 6 day-old embryos. These embryos are either leftover embryos in fertility clinics or embryos created specifically for harvesting stem cells by therapeutic cloning. Only South Korean scientists claim to have successfully created human embryos via therapeutic cloning and have harvested stem cells from them.
Adult stem cells are already designated for a certain organ or tissue. Some adult stem cells can be coaxed into or be reprogrammed into turning into a different type of specialized cell within the tissue type – for example, a heart stem cell can give rise to a functional heart muscle cell, but it is still unclear whether they can give rise to all different cell types of the body.
The primary role of adult stem cells is to maintain and repair the tissue in which they are found.
Uses of Stem Cell Research:
Regenerative (reparative) medicine uses cell-based therapies to treat disease.
Scientists who research stem cells are trying to identify how undifferentiated stem cells become differentiated as serious medical conditions, such as cancer and birth defects, are due to abnormal cell division and differentiation.
Scientists believe stem cells can be used to generate cells and tissues that could be used for cell-based therapies as the need for donated organs and tissues outweighs the supply.
Stem cells, directed to differentiate into specific cell types, offer the possibility of a renewable source of replacement cells and tissues to treat diseases, including Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s diseases, spinal cord injury, stroke, burns, heart disease, diabetes, osteoarthritis, and rheumatoid arthritis.
Read More…